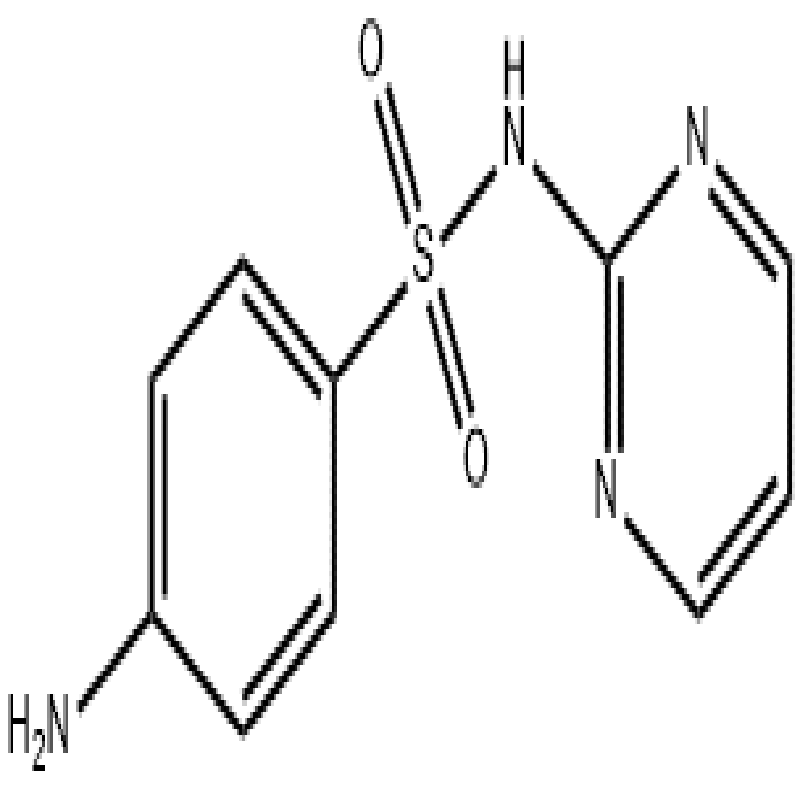
Sulfadiazine CAS#68-35-9
Sulfadiazine (also known as sulfadiazine and diazine) is a clinically common sulfonamide anti-infective in China. Its molecular structure resembles para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA), allowing it to compete with PABA for bacterial dihydrofolate synthase. This competition blocks bacterial folic acid synthesis (using PABA as a precursor), reducing tetrahydrofolate levels—an essential substance for bacterial purine, thymidine, and DNA production—thereby inhibiting bacterial growth and reproduction. It exerts inhibitory effects on susceptible bacteria (e.g., hemolytic streptococci, staphylococci, meningococci, pneumococci, gonococci, Escherichia coli, Shigella dysenteriae) and microorganisms like Chlamydia trachomatis, actinomycetes, Plasmodium, Nocardia asteroides, and Toxoplasma.
Sulfadiazine Chemical Parameters
Melting point | 253 °C (dec.) (lit.) |
Boiling point | 512.6±52.0 °C(Predicted) |
density | 1.3780 (rough estimate) |
refractive index | 1.6440 (estimate) |
storage temp. | 2-8°C |
solubility | Soluble in dimethyl sulfoxide. |
pk | pKa 2.21(H2O t = 25 I = 0.5 (NaCl)) (Uncertain) |
form | powder |
color | white |
Water Solubility | 67.13mg/L(25 ºC) |
Merck | 148903 |
BRN | 6733588 |
BCS Class | 45750 |
CAS DataBase Reference | 68-35-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
NIST Chemistry Reference | Sulfadiazine(68-35-9) |
EPA Substance Registry System | Benzenesulfonamide, 4-amino-N-2-pyrimidinyl- (68-35-9) |
Safety Information | |
Hazard Codes | Xn,Xi |
Risk Statements | 22-36/37/38-42/43-43-42 |
Safety Statements | 26-36 |
RIDADR | 3249 |
WGK Germany | 3 |
RTECS | WP1925000 |
F | 10 |
TSCA | Yes |
HazardClass | 6.1(b) |
PackingGroup | III |
HS Code | 29335990 |
Toxicity | LD50 oral in mouse: 1500mg/kg |
Sulfadiazine CAS#68-35-9 Application
As a top-tier sulfonamide antibiotic, it boasts potent antibacterial and astringent effects, along with good efficacy, rapid absorption, slow excretion, and high effective blood concentrations. Clinically, it treats infections like upper respiratory tract infections, epidemic meningitis, otitis media, furuncles, puerperal fever, urinary tract infections, and acute bacillary dysentery—targeting pathogens including hemolytic streptococci, pneumococci, meningococci, gonococci, and Escherichia coli. Its mechanism of action involves inhibiting prokaryotic folic acid synthesis by blocking dihydropteroate synthase, thus preventing dihydropteroate production.
Factory Show
As an ISO-certified chemical exporter with 15 years of professional experience, we leverage leading production technology, advanced equipment, and a professional team to provide high-quality chemical raw materials to over 2,000 companies worldwide. Our products are widely used in pharmaceuticals, agriculture, food manufacturing, and industrial production, with business spanning six continents. We are committed to providing reliable supply chain support and solutions to customers across various industries.